Easy Future Tense: Definition and Examples
Once we speak or write about plans, expectations, schedules, and predictions, we frequently use the straightforward future tense. The easy future tense helps convey an motion or state that may start and finish sooner or later:
This 12 months, Safiya will learn forty books.
It will likely be onerous, however she is decided to do it.
What’s the easy future tense?
The easy future tense is shaped utilizing the auxiliary verb will with a primary verb. The method is will + [root form of main verb]:
I will be taught a brand new language.
Safiya will learn that e book.
My brothers will sleep till midday if nobody wakes them up.
You will see what I imply.
As you possibly can see from the above examples, will is conjugated the identical means whatever the sentence’s topic in particular person or quantity. In contrast to verbs in lots of different languages, English verbs don’t change kind, which is named a conjugation. The phrase “will” is the one factor wanted to convey that the motion takes place sooner or later. This rule additionally signifies that you solely want to make use of the basis type of the primary verb. They don’t require a suffix like -ed, which connotes an motion that occurred prior to now.
Easy methods to use the straightforward future tense
The easy future in declarative sentences
We use the straightforward future tense in declarative sentences to state that one thing is scheduled or deliberate. It communicates willingness and expresses an expectation, a prediction, or a guess:
The bundle will arrive subsequent Tuesday.
Frey will carry out the lead function within the play.
I can have extra data for you the subsequent time we speak.
It will rain earlier than lengthy.
Mei thinks she will hear again concerning the job she simply utilized for.
I will gladly present you round city while you arrive.
Making the straightforward future damaging
To point that one thing received’t occur, observe the same method however add the phrase “not” to point the damaging: will + not + [root form of main verb].
The bundle won’t arrive in time for the celebration.
I won’t end washing the dishes earlier than I’ve to depart for sophistication.
Safiya won’t stop earlier than she reaches her aim.
Be sure to arrive on time tomorrow as a result of the bus won’t wait for you.
They won’t inform us something about their new pal.
Asking a query within the easy future
The method for asking a query within the easy future is will + [subject] + [root form of main verb].
Will Safiya end studying forty books by the top of the 12 months?
Will I’ve time to complete washing the dishes?
What will Arif do with the cash he received for his birthday?
Will you go to the films with me this weekend?
The easy future vs. different future types
Be going to
One other frequent option to present that one thing will start and finish sooner or later is by utilizing be going to. The be going to building follows the method am/is/are + going to + [root form of main verb]:
I am going to be taught a brand new language.
Safiya goes to learn that e book.
My brothers are going to sleep until midday if nobody wakes them up.
You are going to see what I imply.
The be going to building is just like the will building. It’s used to debate acts or situations that may start and finish sooner or later. Nevertheless, it’s typically extra casual and conversational.
Be going to can be extra possible for use when a author or speaker desires to emphasise a choice they’re making within the current about their intentions, whereas will is extra generally used for stating a reality concerning the future:
I am going to see what I can discover out about that job for you.
You will get a name from the hiring supervisor about that job tomorrow.
To make sentences utilizing be going to damaging, the method is am/is/are + not + going to + [root form of main verb]:
Safiya is just not going to stop earlier than she reaches her aim.
To kind questions utilizing be going to, the method is am/is/are + [subject] + going to + [root form of main verb]:
What is Arif going to do with the cash he received for his birthday?
Current tenses used for the longer term
In casual English, one thing that may undoubtedly occur sooner or later is typically described utilizing the easy current or the current steady tense, whereas further context reveals when the motion takes place:
My favourite tv present airs in half an hour.
Vera is having dinner with Xavier subsequent week.
The longer term steady
The future steady tense ([will be] + [present participle of main verb]) communicates that we count on an motion or state to be in progress at a particular time sooner or later, or that it’ll start after which be ongoing:
By the point you learn this letter, I will likely be boarding my prepare.
After subsequent week, the Kims will likely be dwelling in a brand new city.
The longer term good
The future good tense ([will have] + [past participle of main verb]) refers to an motion or situation that’s anticipated to be accomplished by a sure time or earlier than one thing else occurs:
Subsequent June, it can have been ten years because the twister touched down in our neighborhood.
The prepare can have arrived on the Philadelphia station by 5 o’clock.
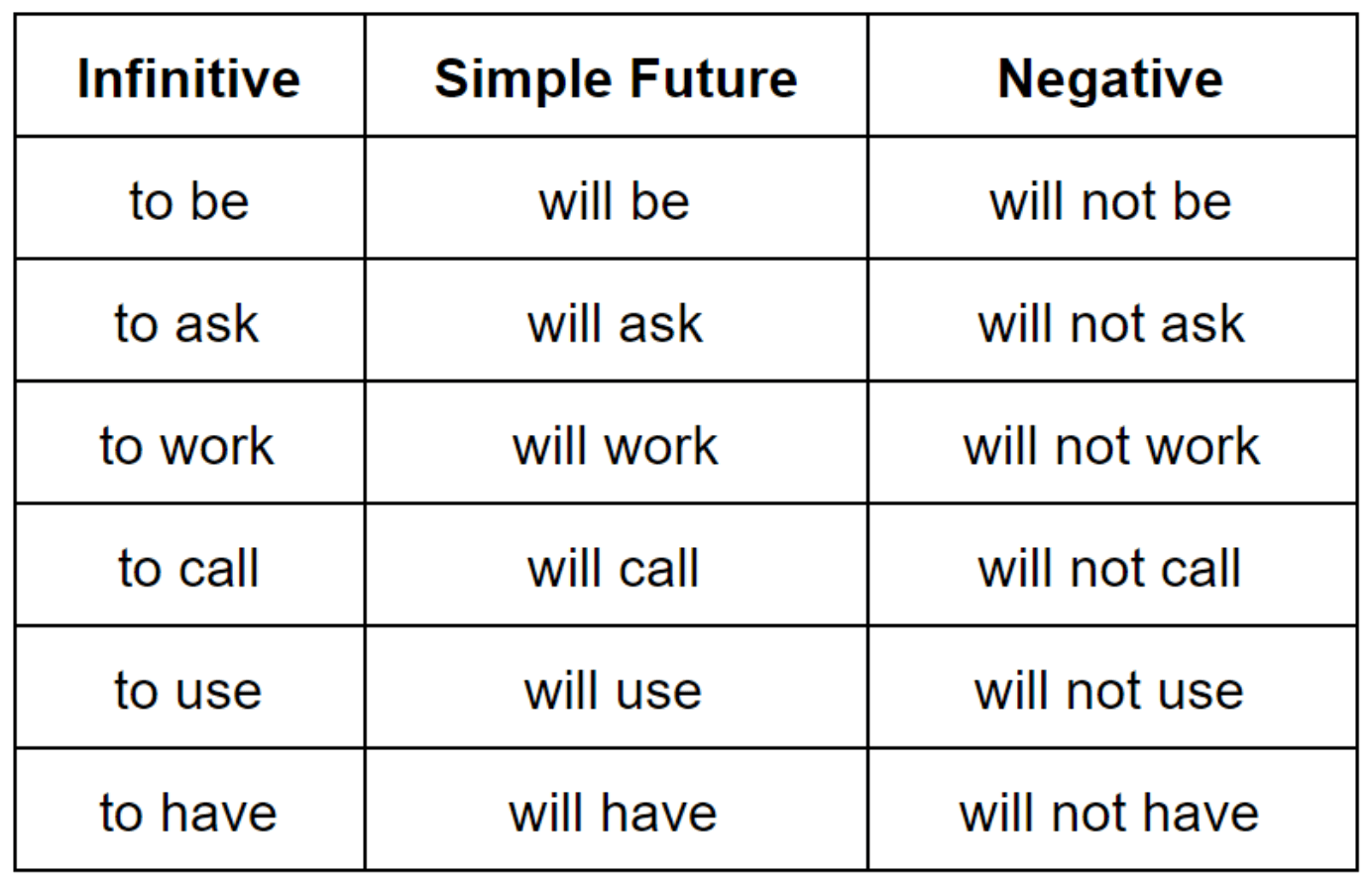
Frequent verbs within the easy future tense
Easy future FAQs
What’s the easy future tense?
The easy future is a verb tense used to speak about an motion or state that may start and finish sooner or later. It makes use of the auxiliary verb will and a primary verb.
How is the straightforward future tense shaped?
The method for the straightforward future tense is will + [root form of main verb].
Do verbs inside the easy future tense change kind based mostly on their topic in quantity and particular person?
No. All verbs within the easy future are conjugated the identical means—will + [root form of main verb]—no matter their topic in quantity and particular person.
What are some methods apart from the straightforward future tense to speak about issues that may occur sooner or later?
In addition to the straightforward future, there are just a few different future types. Be going to, the straightforward current tense, and the current steady tense are all typically utilized in casual contexts for the longer term. In all contexts, English additionally has the longer term steady textual content and the longer term good tense.

