Information Domains For The twenty first Century Pupil

by TeachThought Employees
Considering within the twenty first century is simply completely different.
That doesn’t imply we’re all immediately all-powerful cyborgs, nor can we all change into senseless social media addicts who spend our cognitive may tapping, swiping, and drooling on our smartphone and pill screens.
However simply because the nineteenth century introduced distinctive challenges to info processing in comparison with the 18th or twentieth, the twenty first century is completely different from the one earlier than it or from the one that may come after.
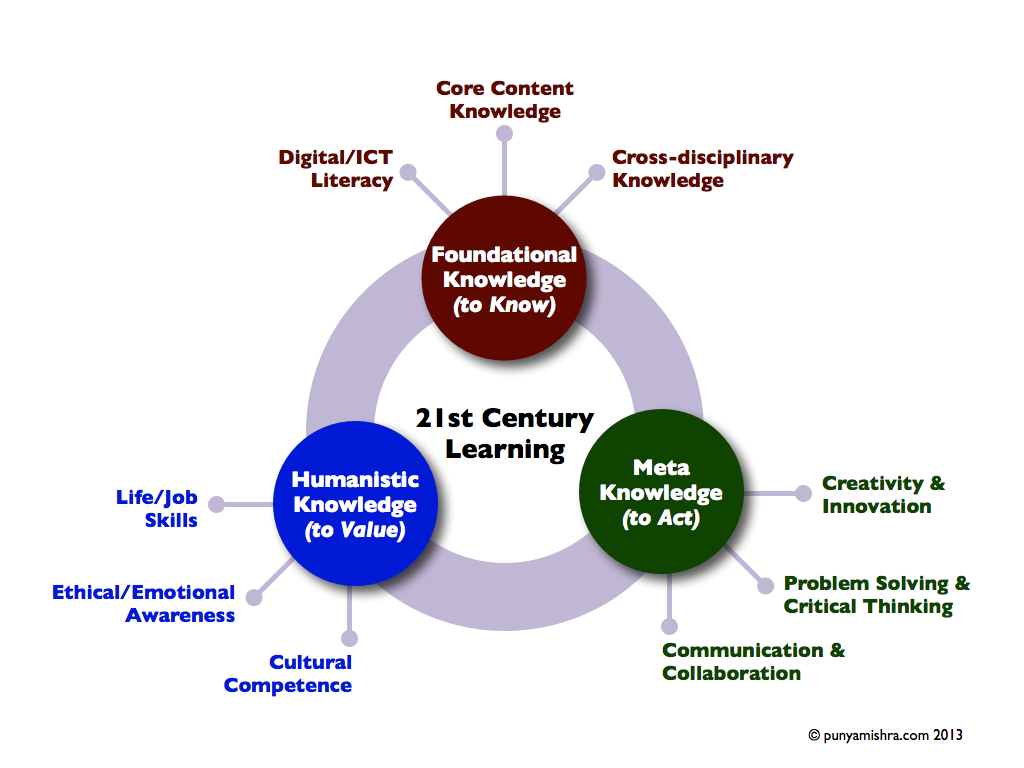
punyamishra.com lately launched the next graphic, which I believed was fascinating. It recognized information varieties for contemporary studying, selecting Foundational, Humanistic, and meta information.
3 Information Domains For The twenty first Century Pupil
1. Foundational Information (To Know)
Digital/ICT Literacy, Core Content material Information, Cross-disciplinary Information
Abstract
This area encompasses the basic ideas and ideas that kind the premise of varied fields of research. It consists of topics comparable to arithmetic, pure sciences, historical past, and language arts. Foundational information gives the framework for understanding extra specialised areas of information and is essential for crucial pondering, problem-solving, and communication abilities.
Examples Of Foundational Information
Instance 1: In a math classroom, college students can study foundational ideas comparable to addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division by hands-on actions like visualizing mathematical operations utilizing manipulatives (comparable to blocks or counters).
Instance 2: Lecturers can introduce foundational information of chemistry by conducting hands-on experiments to discover the properties of various components, compounds, and chemical reactions, comparable to mixing acids and bases to look at modifications in pH.
Instance 3: Lecturers can introduce foundational information of world historical past by analyzing timelines and maps to hint the most important occasions, actions, and empires which have formed world civilizations over time.
Instance 4: Lecturers can combine humanistic information by analyzing the characters, motivations, and moral dilemmas introduced in literary texts, encouraging college students to empathize with numerous views and experiences.
Instance 5: College students can find out about foundational ideas in physics by conducting experiments to know Newton’s legal guidelines of movement, utilizing easy supplies like ramps, balls, and spring scales.
2. Humanistic Information (To Worth)
Life/Job Abilities, Moral/Emotional Consciousness, Cultural Competence
Abstract
Humanistic information focuses on learning human experiences, values, and cultures. It consists of literature, philosophy, artwork, faith, and ethics disciplines. Humanistic information helps people discover questions of which means, identification, morality, and social justice, fostering empathy, creativity, and a deeper understanding of the human situation.
Examples Of Humanistic Information
Instance 1: College students can use artistic writing workout routines to specific their ideas, feelings, and insights, drawing inspiration from literary works and private experiences to discover themes of identification, belonging, and self-discovery.
Instance 2: Lecturers can facilitate philosophical discussions on timeless questions comparable to the character of actuality, the which means of life, and the existence of free will, encouraging college students to look at their very own beliefs and assumptions critically.
Instance 3: College students can have interaction in debates and Socratic dialogues to discover moral dilemmas and ethical reasoning, making use of philosophical ideas to real-world points and moral decision-making.
Instance 4: Lecturers can combine humanistic information by encouraging college students to create paintings impressed by magnificence, love, battle, and transformation, utilizing varied media and strategies to specific their concepts and feelings.
3. Meta Information (To Act)
Creativity and Innovation, Drawback-Fixing and Vital Considering, Communication and Collaboration
Abstract
Meta-knowledge refers to information about information itself—the processes, constructions, and methods concerned in buying, organizing, and evaluating info. It encompasses crucial pondering abilities, info literacy, analysis methodologies, and metacognition. Meta information empowers people to change into lifelong learners, adapt to altering environments, and make knowledgeable selections in a quickly evolving world.
Examples
Instance 1: In any topic space, lecturers can incorporate crucial pondering abilities by posing open-ended questions that require college students to research info, consider proof, and assemble reasoned arguments supported by proof and logic.
Instance 2: Lecturers can use case research or real-world eventualities to problem college students to use crucial pondering abilities to advanced issues and decision-making conditions, encouraging them to contemplate a number of views and weigh the implications of their selections.
Instance 3: College students can use metacognitive instruments comparable to idea maps, graphic organizers, or studying journals to prepare and overview their ideas, join new info with prior information, and determine patterns or gaps of their understanding.
Utilizing This Mannequin In Your Classroom
The only manner to make use of this sort of mannequin in your classroom is to contemplate it a framework for planning, whether or not on the unit, lesson, or exercise degree. In that manner, you might attempt to have a stability throughout the three information domains, or one unit closely pursuant of Humanistic Information (a To Kill A Mockingbird novel research, for instance), whereas one other project-based studying unit focuses on Meta Information.
However on a broader and maybe extra subjective degree, this graphic can function a easy reminder that our jobs as lecturers are to assist college students perceive find out how to know, worth, and act, regardless of that almost all of those appear to transcend widespread classroom evaluation instruments.
The idea of information domains can assist the event of crucial pondering abilities. College students can study to research and consider info, determine patterns, and conclude by partaking with domains (certainly one of many) like foundational information. Humanistic information promotes empathy, perspective-taking, and the flexibility to contemplate numerous viewpoints, whereas meta-knowledge fosters metacognition, info literacy, and the capability to assume reflectively about one’s pondering course of.
The large concept of all studying then might begin with figuring out, which ends up in valuing, which informs motion in related and genuine communities.

