What’s Story Construction? 8 Sorts You Ought to Know
Earlier than writing a narrative, it is best to decide the story construction you need to comply with. Story construction serves as a literary blueprint, guiding writers to captivate readers by together with all very important story parts.
Whereas this may sound like Mad Libs, a number of the most well-known authors, playwrights, and different storytellers use these storytelling constructions. You’ll be able to leverage story constructions to boost the plot, characters, and backstory, crafting a story readers can’t put down.
On this weblog, we’ll outline what a narrative construction is, clarify why it’s vital, and supply examples of probably the most generally used varieties.
Desk of Contents
Why story construction is vital
Suggestions for figuring out story constructions
What’s story construction?
Story construction, typically referred to as narrative or plot construction, is the framework inside which the narrator tells a narrative. Writers use story construction as a template to make sure they’ve all the things wanted to inform a transparent and entertaining story from starting to finish.
Following a narrative construction ensures that you just embrace vital particulars and keep away from pointless parts that may distract or bore the reader.
Whereas writers generally use them, story constructions are additionally utilized by public audio system, information anchors, filmmakers, and anybody with a narrative to inform. In truth, a number of the examples we’ll cowl date again to historical Greece.
Earlier than we proceed, it’s vital to notice that story construction is completely different from story archetypes. Archetypes are common patterns or character varieties, whereas construction refers to how these archetypes’ tales are informed. As an illustration, rags to riches is an archetype that may be informed by means of completely different story constructions.
Why story construction is vital
Story construction acts as the inspiration of a story. It ensures continuity, ensures that key themes and particulars are addressed, and helps the author pinpoint important literary parts like battle or plot.
In different phrases, it helps create higher tales. With no correct construction, readers may get misplaced or confused and be tempted to place your e-book down. It helps convey key factors, like the primary battle or general theme, that maintain them excited to proceed studying.
Parts of story construction
Exposition
The exposition lays out the backstory, characters, setting, and plot. It must also introduce the protagonist. An instance can be the primary few pages of The Starvation Video games, during which the reader is launched to Katniss Everdeen, the world of Panem, and the idea of the Starvation Video games.
Rising motion
An inciting incident sometimes causes the rising motion, or the occasion that causes a battle. This story component ought to have pressure and penalties for the protagonist. The inciting incident in The Starvation Video games is Katniss volunteering for her sister, and the rising motion consists of the battles and tribulations she goes by means of through the Starvation Video games.
Climax
The climax is when the protagonist succeeds or typically fails within the battle introduced all through the story. It’s additionally the scene that your entire e-book has been main as much as. In The Starvation Video games, this might be Katniss’s profitable takedown of the federal government.
Falling motion
Falling motion is the consequence or results of the climax. It’s the half in The Starvation Video games the place Katniss returns residence after ending the Starvation Video games and tries to stay a standard life.
Decision
Also referred to as the “denouement,” the decision clears up any free ends and explains how the protagonist and their world have modified due to the plot. In The Starvation Video games trilogy, this might be the ultimate chapter that describes Katniss’s life within the years after the climax.
Sorts of story constructions
Fichtean Curve
Three-Act
Inciting incident: One thing occurs to get the plot shifting.
Plot level one: The protagonist decides to interact within the battle.
Rising motion: There may be pressure between the protagonist and the antagonists.
Midpoint: The protagonist is nearly foiled of their mission to resolve the battle.
Climax: There’s one other confrontation with the antagonist.
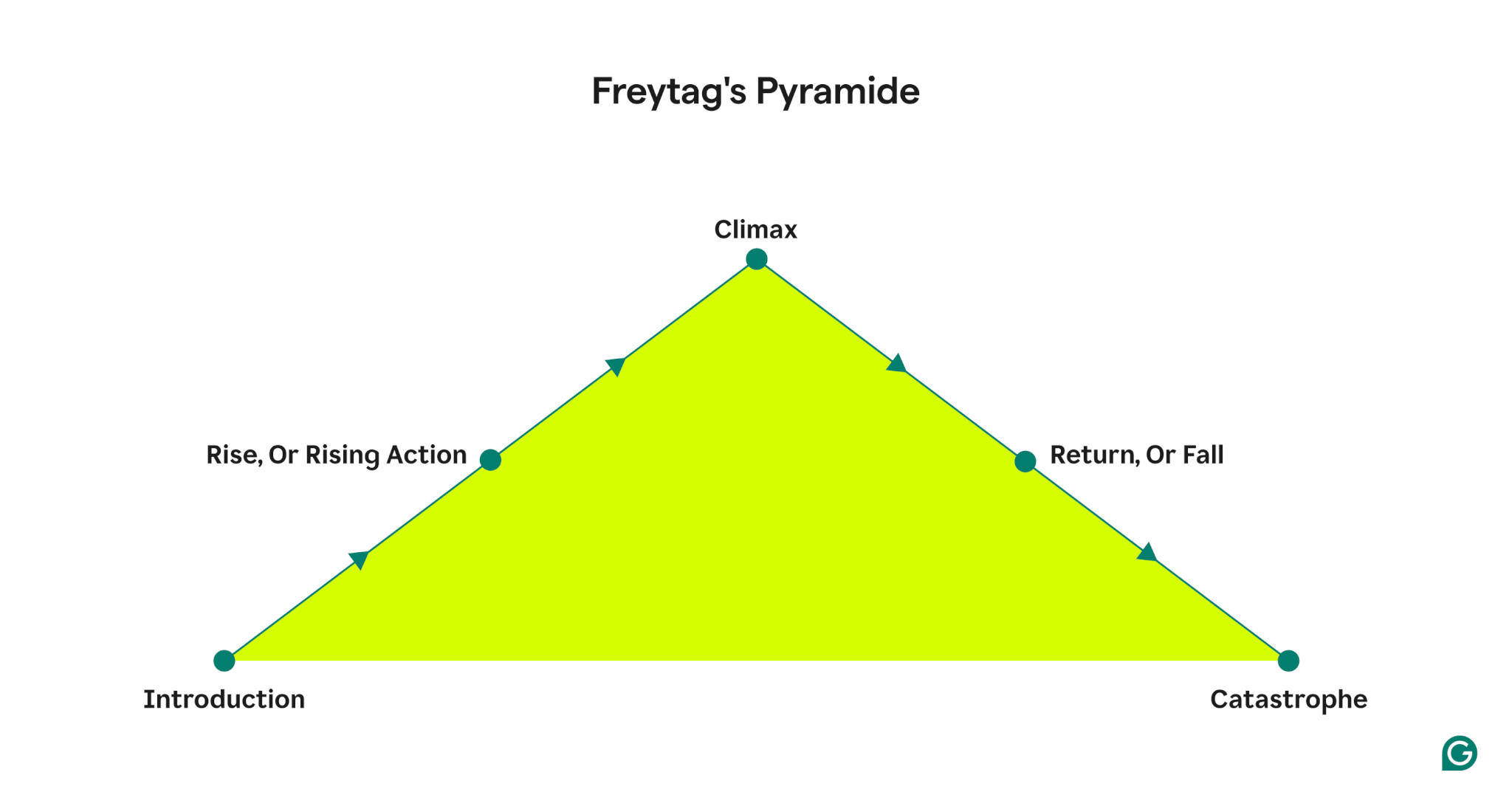
Freytag’s Pyramid
Climax: The battle should be resolved now. That is the purpose of no return.
Falling motion: The implications of the climax.
5-Act
Exposition: The established order and fundamental plot premise are launched.
Rising motion: The protagonist faces a sequence of challenges.
Climax: The purpose of no return
Falling motion: The fallout from the climax
Hero’s Journey
The Hero’s Journey was first utilized in historical mythology and might even be present in trendy examples like Star Wars. There are 12 steps to the Hero’s Journey.
Abnormal world: The hero’s establishment is launched.
Name of journey: An inciting incident that calls on the hero to tackle new challenges outdoors their consolation zone.
Refusal of the decision: The protagonist is, at first, reluctant to tackle these challenges.
Assembly the mentor: The protagonist meets a instructor, guardian determine, or religious chief to assist them on their journey.
Crossing the primary threshold: The character, maybe for the primary time of their life, steps out of their consolation zone.
Checks, allies, enemies: They tackle challenges, meet new associates, and are launched to enemies they’ll combat alongside the best way.
Method to inmost cave: The protagonist approaches their aim.
The ordeal: A combat or take a look at the protagonist engages in and wins.
Reward (seizing the sword): The protagonist obtains a brand new weapon or ability to assist them with their aim.
The street again: The protagonist realizes there’s nonetheless extra work to be finished.
Resurrection: The climax or the ultimate problem the protagonist should face.
Return with the elixir: That is the falling motion and determination, the place the protagonist emerges victorious and takes on a brand new life of their world.
Story Circle

Story Circle is a narrative construction generally utilized by screenwriters and popularized by Dan Harmon, the creator of Rick and Morty and Group. It borrows from the Hero’s Journey construction with out requiring the protagonist or different characters to be remodeled, although the viewers can nonetheless be taught extra about them by means of the rising actions they expertise every episode.
Utilizing any such story construction requires the author to have an intimate understanding of the character they’re making an attempt to write down about and the character arc they need to convey to the viewers. It follows eight fundamental steps:
Zone of consolation: The character is in a establishment.
Need or want: The protagonist needs or wants one thing, which may end result from an inciting incident.
Unfamiliar state of affairs: The protagonist should seek for the factor they need or want in an unfamiliar setting or state of affairs.
Adapt: They start to acclimate to their environment.
Discover: They get the factor they had been looking for.
Pay a heavy value: They notice it won’t have been well worth the bother.
Return to establishment: They return to their zone of consolation.
Change: They’re modified by the unfamiliar state of affairs they had been in.
Seven-Level

The seven-point arc is a story story construction that resembles the Hero’s Journey or Three-Act constructions, although it’s much less strict in how the author maps out the story.
The hook: In the course of the exposition, one thing ought to draw the reader in and make them need to proceed.
Plot level one: An inciting incident or name to journey that causes the protagonist to go away their consolation zone.
Pinch level one: The protagonist meets the antagonist, and their battle is revealed. The antagonist decides it’s their mission to resolve the problem.
Midpoint: The protagonist goes from being a passive to an energetic participant within the battle.
Pinch level two: The protagonist and antagonist meet once more, however the latter wins and seemingly
leaves the great man defeated.
Plot level two: The protagonist discovers one thing that reinvigorates their spark to resolve the battle.
Decision: The battle is resolved, and the protagonist’s character arc is tied up, exhibiting how they’ve modified from the start to the tip.
Save the Cat

The Save the Cat construction is primarily for screenplays as a result of it’s laid out as a beat sheet with web page numbers to point out what number of pages of a screenplay every half ought to take up. That stated, it may be simply tailored to books or quick tales.
Opening picture: The opening shot or paragraph that describes the world the story is happening in.
Setup: What’s the day by day lifetime of your protagonist? What characters do they frequently work together with?
Theme acknowledged: What’s the theme of their story?
Catalyst: The inciting incident
Debate: The protagonist ignores the decision to journey.
Break into two: The protagonist decides to interact within the battle.
B story: A subplot, often comedic or romantic in nature.
The promise of the premise (enjoyable and video games): The protagonist has a couple of minutes of enjoyable
earlier than they’re pushed into the battle.
Midpoint: A plot twist within the protagonist’s journey to resolve the battle.
Unhealthy guys shut in: Elevated battle and pressure attributable to advances from the antagonist
All is misplaced: The protagonist seemingly loses their battle.
Darkish evening of the soul: The protagonist hits all-time low.
Break into three: The protagonist learns new info that reinforces their spirit and confidence.
Finale: The protagonist makes use of their new info to defeat the antagonist within the climax.
Last picture: The decision. A brand new world and a remodeled protagonist are proven to the viewers.
Suggestions for figuring out story constructions
Story constructions FAQs
What are the weather of story construction?
What’s the three-act construction?